


How nad+ and mitochondria works in anti aging solutions

3 mins to read
Recent progress on the roles of NAD+ in aging
NAD+ levels appear to decrease with aging in a variety of tissues, including the skin, lungs, spleen, kidney, liver, skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, heart, brain, kidney, pancreas, and kidney. In addition, it is stated that the levels of NAD+ decrease with age in tissues from Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans), mice, and human post-mortem bodies. indicating a consistent, age-dependent decline in NAD+ among all species. It is unclear, nevertheless, whether this is because NAD+ production is being reduced or used more often . This section gives an overview of techniques that could increase endogenous NAD+ levels.
Abundant Evidence for Anti-aging and Health-Enhancing Effects of nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN)
NMN has shown a wide range of outstanding benefits in several animal models of disease and aging, benefiting disorders including diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, and ischemia. In mouse tissues, NMN taken orally is promptly converted to NAD+. Age-related weight gain has been prevented by NMN, which has also been shown to increase energy metabolism and physical activity, improve insulin sensitivity, ocular function, and mitochondrial metabolism. NMN enhanced the activity and secretion of insulin in obese or diabetic mice. The mouse heart was shielded by NMN from ischemia and/or reperfusion damage. By enhancing energy metabolisms, it has helped old mice recover their skeletal muscle and reduced cognitive loss in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease.
NAD+ Repletion and Aging
Progressive tissue degradation and atrophy brought on by diminished somatic or stem cell activity is one of the main causes of aging. Adult stem cell function are crucial for the regeneration of both typically dormant tissues (like skeletal muscle and the brain) that need to be repaired after injury or disease exposure, as well as continually growing tissues (like the hematopoietic, intestinal, and epidermal systems). In both young and elderly mice, NR supplementation increased metabolic activity in muscle and neural stem cells, extending longevity. Aged mouse stem cells have been demonstrated to be rejuvenated by NR therapy, and the diminished capacity to heal gut injury has been restored. Previous research has demonstrated that NR supplementation can lessen the DNA damage that occurs to mouse nerve cells, nerve stem cells, and muscle stem cells. Additionally, NR has been demonstrated to reduce mitochondrial dysfunction, increase oxidative metabolism, and extend the lifetime of obese mice through neuronal DNA repair and improved mitochondrial quality.
Anti-aging effects of NAD+
Through its role as a substrate for sirtuins, CD38, and PARP, NAD+ regulates a variety of cellular process including energy metabolism, DNA damage repair, gene expression, and oxidative stress response.
Within the cell, NAD+ and NADH are in a dynamic equilibrium. Through oral administration of NAD+ precursor or by preventing NAD+ breakdown, intracellular NAD+ can be elevated in vivo. This type of regulation of the NAD+/NADH ratio has been proven to alleviate senile deafness in old mice and can enhance mitochondrial activity.
NAD+ Repletion and Aging
Progressive tissue atrophy and degeneration brought on by diminished somatic or stem cell activity is one of the main causes of aging. Adult stem cells are necessary for both continually growing tissues (like the hematopoietic, intestinal, and epidermal systems) and typically dormant tissues (like the brain and skeletal muscle) that need to regenerate after injury or disease exposure. In both young and elderly mice, NR supplementation increased metabolic activity in muscle and neural stem cells, extending longevity. Aged mouse stem cells have been demonstrated to be rejuvenated by NR therapy, and the diminished capacity to heal gut injury has been restored. Previous research has demonstrated that NR supplementation can lessen the DNA damage that occurs to mouse nerve cells, nerve stem cells, and muscle stem cells. Additionally, NR has been demonstrated to reduce mitochondrial dysfunction, increase oxidative metabolism, and extend the lifetime of obese mice through neuronal DNA repair and improved mitochondrial quality.
Potential Benefits
NAD+ is crucial for maintaining a species’ mitochondria and regulating aging-related genes. However, as we age, our body’s amount of NAD+ significantly decreases.
According to studies, the molecule’s decline is linked to age-related illnesses such accelerated aging, metabolic problems, heart disease, and neurodegeneration. Because the metabolism is less functioning as we age, low levels of NAD+ are linked to age-related diseases. However, raising NAD+ levels has demonstrated anti-aging benefits in animal models, demonstrating promising outcomes in the reversal of age-related illnesses, extending longevity, and improving health.
Aging
Sirtuins, sometimes referred to as “guardians of genomes,” are genes that shield all types of organisms—from plants to mammals—against degradation and illness. The genes dispatch troops to protect the body when they detect physical stress, such as exercise or hunger. Sirtuins maintain genomic integrity, encourage DNA repair, and have been linked to anti-aging effects in model animals, such as lengthening longevity.
The energy source for the genes’ operation is NAD+. But sirtuins need NAD+ to function, just like a car cannot run without fuel. According to research, increasing the body’s NAD+ level activates sirtuins and lengthens the lives of mice, worms, and yeast. Although NAD+ replenishment has promising outcomes in animal models, researchers are still investigating how these outcomes may apply to people.
Muscle function
As the powerhouse of the body, mitochondrial function is crucial for our exercise performance. NAD+ is one of the keys to maintaining healthy mitochondria and steady energy output.
Mice with higher NAD+ levels have better mitochondria and are more fit. Other studies demonstrate that mice who get NAD+ boosters are slimmer and have more endurance when running on a treadmill. Animals that are older and have more NAD+ perform better than their contemporaries.
Metabolic disorders
Aging and high-fat diet reduce the level of NAD+ in the body. Studies have shown that taking NAD+ boosters can alleviate diet-associated and age-associated weight gain in mice and improve their exercise capacity, even in aged mice. Other studies even reversed the diabetes effect in female mice, showing new strategies to fight metabolic disorders.
-
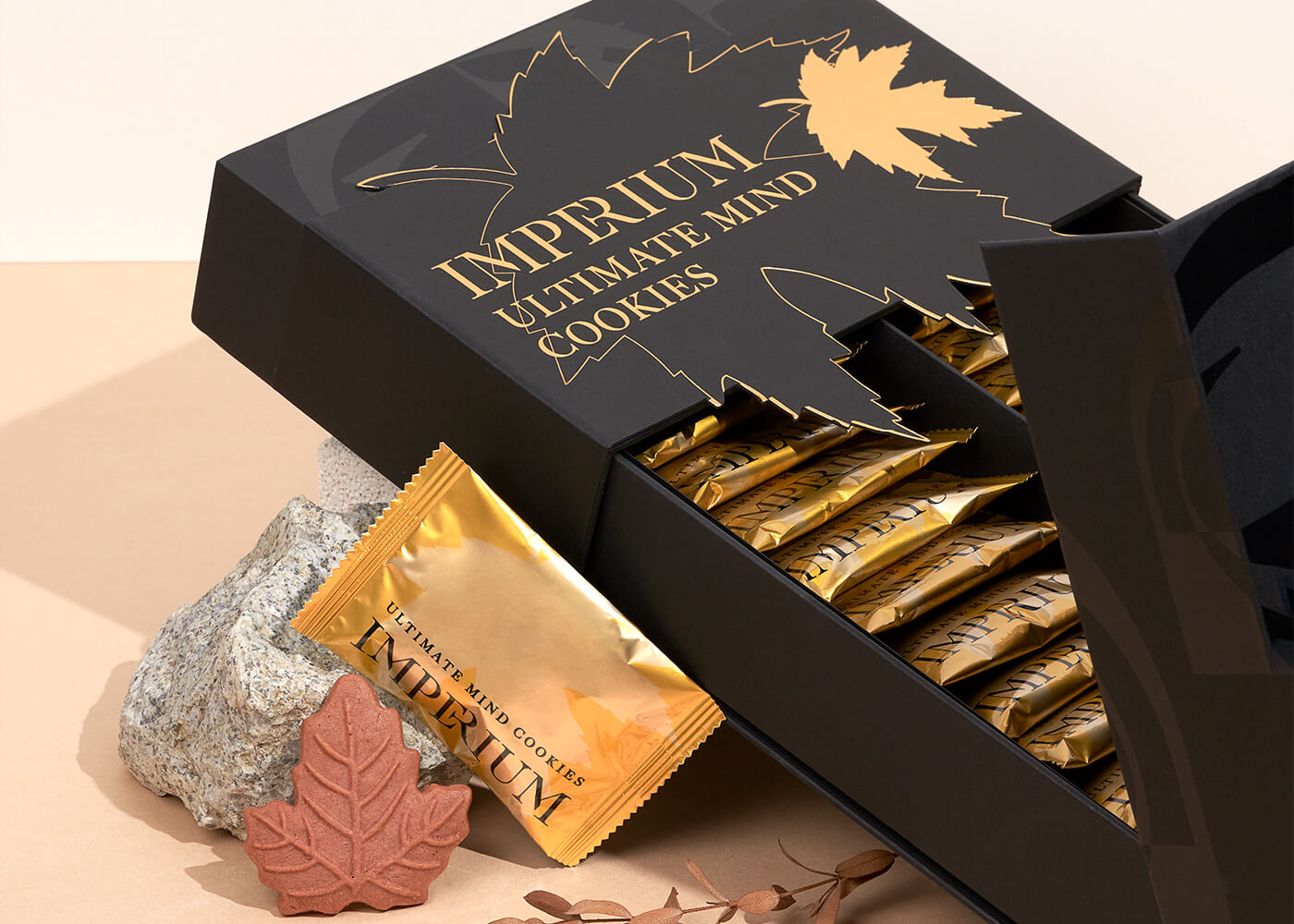

Ultimate Mind
Kick start the day with a packet of Ultimate Mind to boost memory and concentration throughout the day. The Ultimate Mind Cookie is a healthy snack that promotes memory, concentration, and cognitive function. BUY NOW How Do the Brain and Mind Function? The brain is the control centre for the body. It regulates all of […]
-
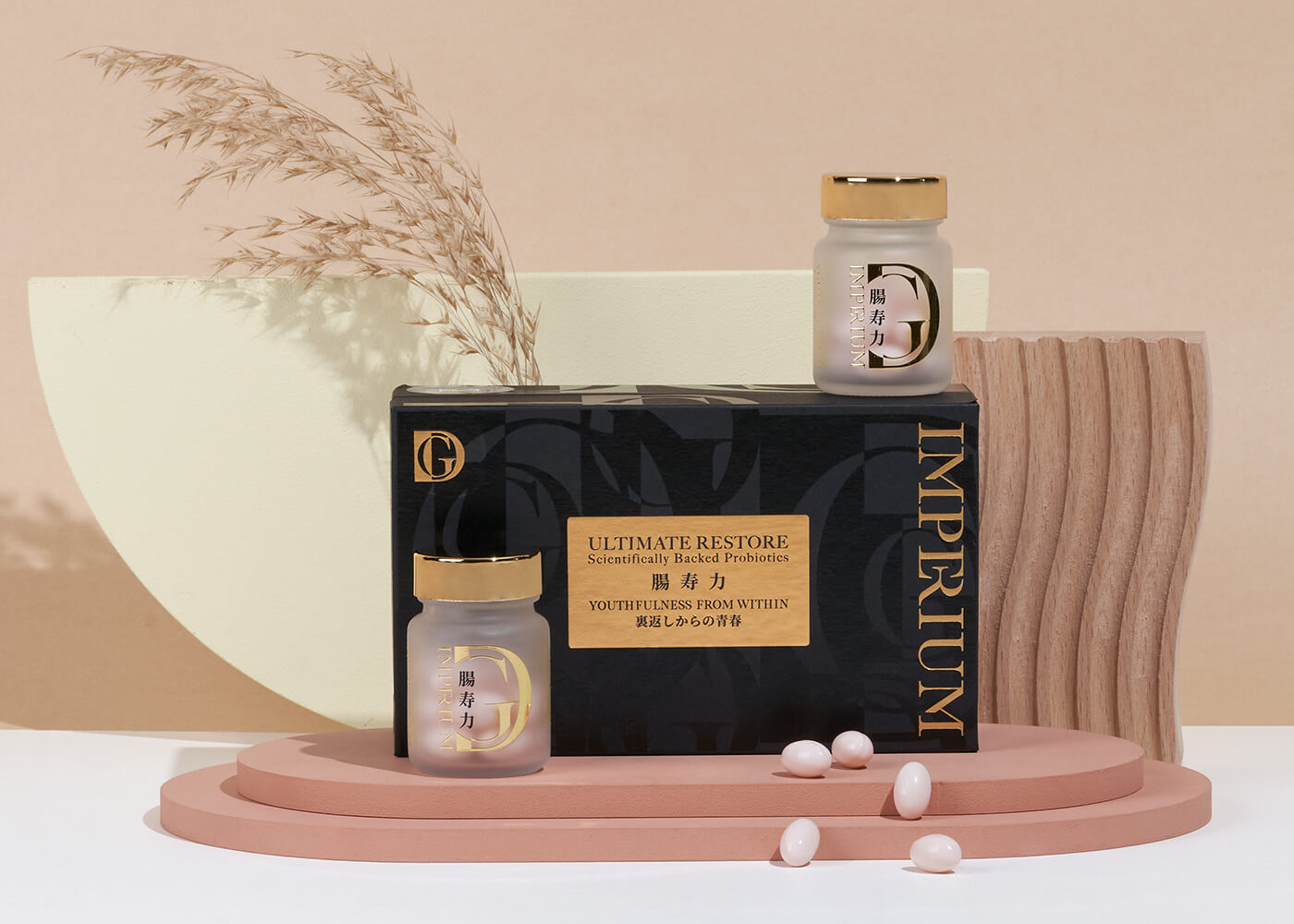

Ultimate Restore
Why is a Healthy Digestive System Important? Good digestive health is essential for good overall health. Your digestive system is responsible for breaking down the food you eat, extracting nutrients, and eliminating waste. The digestive system includes the mouth, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine (colon), rectum, and anus. The entire length of the digestive […]
-

Ultimate Cleanse
The Ultimate Cleanse Meal Replacement is formulated with whole-food nutrition, patented and potent ingredients of more than 55 highly absorbable and functional ingredients and essential nutrients. Packed with fibre and protein, to support detoxification, cellular repair, and cellular rejuvenation. Benefits include maintaining a healthy digestive system, important for detoxification and immune health. Why is a […]